
- Mac os x terminal commandds how to#
- Mac os x terminal commandds install#
- Mac os x terminal commandds code#
Pressing the shortcut again restores the hidden panes. Exit out a pane by typing exit in that pane.Temporarily toggle maximize the current pane (hiding all others) with command-shift-enter.Navigate among panes with command-opt-arrow or cmd+.split window horizontally with Command+Shift+D.Terminal does not support but iTerm2 does support dividing the CLI into several rectangular “panes”, each of which is a different terminal session:
Mac os x terminal commandds install#
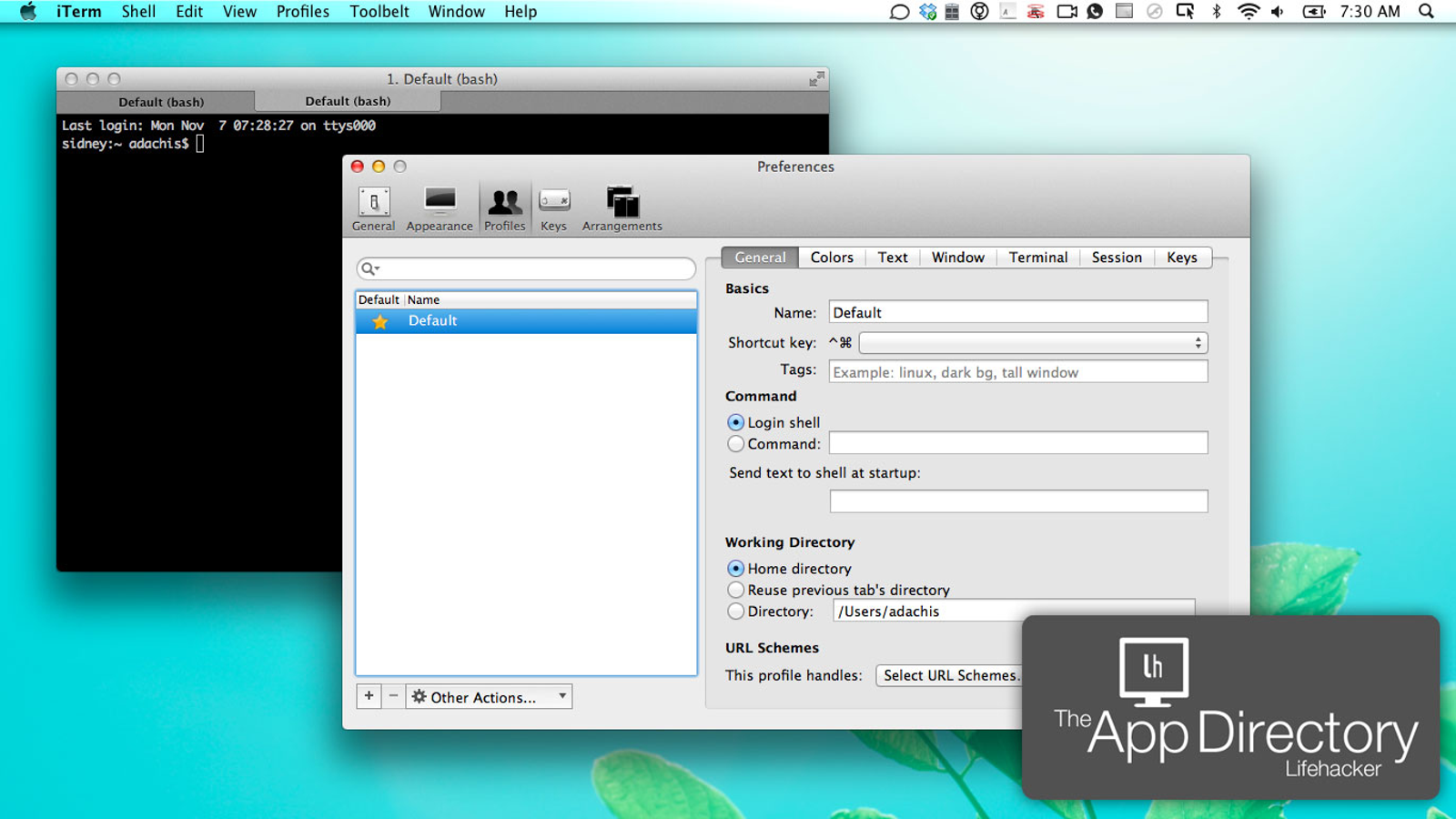
Install iTerm2 using Homebrew: brew install -cask iterm2 Many prefer to install and use iTerm2 instead of the built-in Terminal program.

Build an extension based on hyper.is/#extensions-api. To customize Hyper, add the name of many packages to its config file ~/.hyper.js. It is available on MacOS, Windows, and Linux because it’s built using Electron (the same platform that powers Atom, Slack, and Brave). Unlike Apple’s Terminal, which is closed-source, Hyper is an open-source and extensible terminal emulator.
Mac os x terminal commandds code#
Many prefer the terminals built into VS Code and other editors/IDEs. R is for readable, x is for eXecutable by the user. S shows the symbolic equivalent to “0022” for u=user, g=group, o=others : u=rwx,g=rx,o=rx To identify the User Mask for permissions: umask Please read it for the whole story on this. Wikipedia says umask controls how file permissions are set for newly created files. bash_history lines of command history (500 by default) User Mask for permissions In other words, file /etc/profile is the system wide version of ~/.bash_profile for all users.Įxport HISTSIZE=1000 # sets the size of. PROTIP: One can change those files, but since operating system version upgrades can replace them without notice, it’s better to create a file that is not supplied by the vendor, and within each user’s $HOME folder: ~/.bash_profile Thus, whatever is specified in /etc/profile is NOT invoked for “non-interactive” shells invoked when a user cannot manually interact with it, i.e. RedHat also executes /etc/profile.d if the shell invoked is an “Interactive Shell” (aka Login Shell) where a user can interact with the shell, i.e. NOTE: On Ubuntu, instead of /etc/bashrc, the file is /etc/bash.bashrc. The above defines the $PS1 variable which sets the Terminal’s prompt to the left of the cursor. # Make bash check its window size after a process completes bashrc file for interactive bash(1) shells. The /etc/bashrc file contains: # System-wide.
profile for sh(1)Įcho $ resolves to /usr/local/bin/bash. When macOS logs in a user, it executes file /etc/profile. I put in an echo in the various files that macOS executes upon user login, when a new terminal is opened, and when a bash shell is invoked: In /etc/profile.

Mac os x terminal commandds how to#
This tutorial describes how to make use of the macOS Terminal to make your life easier and less frustrating.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
